AI is now embedded in everyday operations across support, finance, healthcare, and the public sector. As models touch more sensitive data, the legal landscape is moving just as quickly. The center of gravity has shifted from annual checklists to continuous compliance in production. This guide explains the regulatory frameworks affecting AI and data privacy in 2025, how they fit together, and how to turn their requirements into practical, repeatable controls your teams can run every day.
The global map of rules you should know
European Union
EU AI Act: The EU AI Act entered into force on 1 August 2024 and applies in stages. Prohibitions and AI literacy obligations started on 2 February 2025, obligations for general purpose AI models began on 2 August 2025, and most duties for high risk systems apply by 2 August 2026, with embedded high risk rules extending to 2027. The law formalizes risk based obligations and expects documentation, data governance, transparency, and human oversight.
European Health Data Space: The EHDS was published in the EU’s Official Journal on 5 March 2025 and entered into force on 26 March 2025, kicking off a transition toward application over several years. It standardizes access to health records for patients and sets clearer rules for secondary use and research across the EU.
Why this matters: Together, these frameworks push organizations to prove the quality and provenance of training data, restrict risky use cases, and enable safe secondary use with strong de identification and access controls.
United States
There is still no single federal consumer privacy law, so states continue to lead with a patchwork of comprehensive statutes. Keeping track of effective dates and subtle differences has become a standing task for privacy teams operating across multiple states. The IAPP’s tracker confirms ongoing expansion of state level privacy obligations through 2025.
Sector specific rules are also tightening. The Federal Trade Commission finalized amendments to the Health Breach Notification Rule in May 2024 to clearly cover many health apps and connected devices outside HIPAA. In parallel, the US Department of Health and Human Services proposed significant updates to the HIPAA Security Rule to better address modern cyber threats.
China
China refined cross border data transfer rules in 2024, clarifying when assessments or standard contracts are needed, and is moving toward national safety standards for cross border processing that raise technical expectations on exporters. These standards are scheduled to take effect in 2026, so teams should treat residency and transfer logging as live engineering requirements.
India
India’s Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023 is transitioning into practice through guidance and rulemaking. Organizations should prepare for evolving rules on cross border transfers, consent, and data rights as implementing provisions continue to roll out.
International standards and treaties
NIST AI Risk Management Framework and Generative AI Profile: NIST released a Generative AI profile for its AI RMF in July 2024, offering a practical control catalog and shared language that aligns well with many regulatory expectations.
ISO 42001: ISO 42001 establishes a certifiable AI management system and integrates cleanly with ISO 27001 and 27701, giving organizations a governance baseline buyers and auditors recognize.
Council of Europe AI treaty: The Framework Convention on Artificial Intelligence is the first binding international AI treaty, opened for signature in September 2024. It anchors human rights and rule of law principles that many jurisdictions are now echoing in national rules.
How these frameworks fit together
Across regions, the themes are consistent even if the labels differ.
- Lawful basis and consent: Know the legal reason for processing and present clear notices.
- Purpose limitation and minimization: Use the smallest necessary field set for a defined purpose.
- Data quality and documentation: Prove dataset provenance, curation, and testing.
- Transparency and explanation: Offer readable reasons for impactful automated decisions.
- Governance and oversight: Define roles, reviews, and human in the loop checkpoints for high risk uses.
- Security and cross border controls: Encrypt, restrict access by role and purpose, and route by residency with evidence.
The key shift in 2025 is verification. Regulators and enterprise customers want proof that controls run where data flows, not just policy PDFs.
Translate law to controls you can run every day
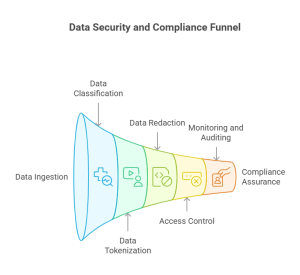
You can satisfy most obligations with a handful of precise controls placed where risk begins.
Ingestion and ETL
- Classify PII, PHI, biometrics, and secrets as data lands
- Tokenize identifiers deterministically and mask high risk fields
- Reject files that contain credentials or keys
Storage and retrieval
- Redact sensitive entities in documents before creating embeddings or indexes
- Tag sources with purpose and residency and filter retrieval by policy
LLM and API gateway
- Scan prompts for risky content and apply output filters for sensitive entities
- Restrict tools to allow lists and use scoped credentials tied to role and purpose
- Enforce response schemas and scopes; rate limit and monitor for anomalies
Logging and monitoring
- Redact logs by default and shorten retention windows
- Baseline vector queries, prompts, APIs, and egress to catch slow exfiltration
Lineage and audits
- Keep dataset registers and join every decision to the user, policy version, and time
- Export evidence for regulator inquiries, customer reviews, and internal audits
These are the building blocks regulators expect under the EU AI Act and related EU health initiatives, US sector rules, and many international standards.
What each region expects in practice
European Union
- Risk classification for AI uses, with stronger obligations on high risk systems
- Documentation packs that cover data governance, testing, post market monitoring, and human oversight
- For health data, stronger rights for patient access and standardization to support secure secondary use under the EHDS
United States
- Varying state requirements for consent, opt outs, profiling, and children’s data
- Sector enforcement, especially in health, where HBNR reaches many apps and devices outside HIPAA and HIPAA Security updates raise the bar for technical safeguards
China and India
- Residency and transfer logic must be coded, not only contracted
- Keep inventories of transfers and mechanisms, tokenize identifiers before export where feasible, and route traffic to allowed regions
International standards
- Map your controls to NIST’s AI RMF and ISO 42001 to create a common language for internal assurance, customer reviews, and regulator discussions.
Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
Indexing before redaction
If raw identifiers make it into your vector store, retrieval will eventually surface them. Redact before embedding and filter retrieval results.
Policies without enforcement
Documents do not block leaks. Put policy in gateways and code paths, and keep logs that show which rule fired.
One time data maps
Your inventory changes weekly. Run continuous discovery and classification.
Over sharing APIs
Endpoints return more fields than necessary. Enforce response schemas and scopes with automated rejections and masking.
Vendor drift
Contracts say one thing, traffic does another. Monitor egress, require no retention options, verify regions, and keep sub processor lists current.
Sector snapshots
Healthcare
Redact PHI before indexing, tokenize MRNs and claim IDs, and maintain clear explanations for decision support. The EHDS increases expectations for standardization and access, while US health rules broaden breach duties for many apps.
Financial services
Prioritize deterministic tokenization for account and card identifiers, enforce API schemas for statements and support workflows, and maintain lineage for audits and investigations.
Public sector and education
Purpose limitation and transparency dominate. Route by residency, maintain plain language explanations and appeals, and keep field level access logs.
Retail and consumer tech
Focus on pre prompt redaction, response schema enforcement, short retention, and easy opt outs. Publish simple explanations of what data powers personalization.
How Protecto helps
Protecto is a privacy control plane for AI and analytics. It places precise controls where risk begins, adapts enforcement to jurisdiction and purpose in real time, and produces the evidence that regulators and enterprise buyers expect under the regulatory frameworks affecting AI and data privacy in 2025.
What Protecto delivers
- Automatic discovery and classification across warehouses, lakes, logs, and vector stores
- Deterministic tokenization for structured identifiers and contextual redaction for free text at ingestion and before prompts
- LLM and API gateways for pre prompt filters, output scanning, schema enforcement, scopes, and rate limits
- Jurisdiction aware policy enforcement for purpose and residency, logged with policy version and context
- Lineage from source to embedding to output for EU AI Act packs, DSAR responses, and partner reviews
- Anomaly detection for vectors, prompts, APIs, and egress, with throttle or block actions
- Developer friendly SDKs and CI checks so privacy becomes part of every build