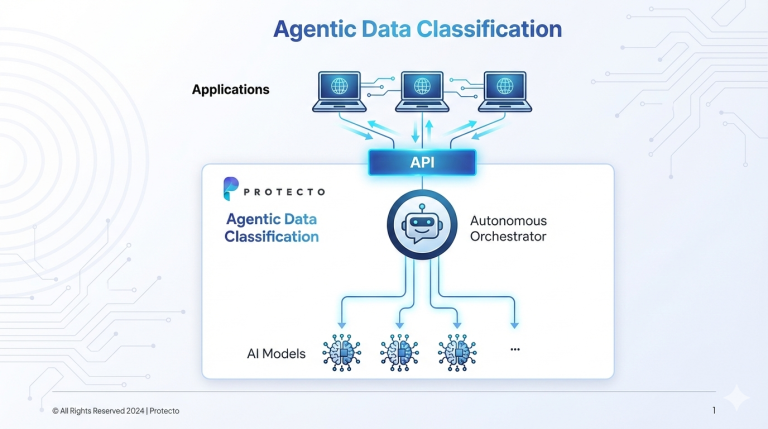
For instance, GDPR (article 30 and 36) requires organizations to document their processing and conduct periodic data protection impact assessments (DPIA). Without a comprehensive data map, organizations can’t comply with these requirements.
A comprehensive data map should have the following basic set of attributes:
- Data inventory – What data is collected?
- Storage – Where is the data stored? Is it secure and encrypted?
- Purpose – Why the data collected for?
- Use – Who has access to the data? Who is using the data?
- Flow – Where does the data flow? Who do we share outside the organization?
- Lifespan – When was it created? How long will data be stored? How will it be disposed of?
- Sensitive data – What sensitive /personal data does the data source hold?
- Data lineage – What data sources were combined or transformed to derive a data asset?
- Additional metadata that is relevant to data protection –
- What are the categories of data subject (customer, employee, partner, contractor) contained?
- What is the geographical location of data subjects in the data?
- Does it have a minor’s data?