Data security demands robust protection methods in our digital age. Format-preserving encryption and tokenization stand out as robust solutions for safeguarding sensitive information. Understanding the difference between data tokenization and encryption helps organizations protect data while maintaining usability.
Modern businesses must choose between encryption vs tokenization for their needs. The choice between these methods impacts system performance and security levels. Security teams need to understand both approaches to make informed decisions.
The rise of data breaches makes these protection methods critical. Organizations need reliable ways to secure sensitive data. Strong security measures protect both business interests and customer trust.
Understanding Format-Preserving Encryption (FPE)
Format-preserving encryption transforms sensitive data into encrypted values. It keeps the original data format and length intact during encryption. For example, a credit card number remains a 16-digit number after encryption.
FPE encryption works through specialized encryption algorithms. These algorithms convert each character while preserving the data structure. The encrypted output matches input constraints like character sets and formats.
How FPE Works
The encryption process starts with data validation. FPE encryption checks the input format requirements. The algorithm then applies encryption while maintaining these format rules.
Every character undergoes secure transformation using strong encryption keys. Multiple rounds of encryption ensure data security.
FPE supports various data types and formats. It works with numerical sequences, text strings, and mixed data, and the method adapts to different business requirements.
Common Use Cases
Banks use FPE to protect account numbers, healthcare providers secure patient IDs with FPE, and retailers protect loyalty card numbers through format-preserving encryption.
Credit card processors encrypt transaction data. Government agencies secure citizen identification numbers. Insurance companies protect policy numbers with FPE.
Benefits of FPE
FPE requires no database changes. Applications continue working with encrypted data, and the method allows quick implementation across existing systems.
FPE supports direct searching and sorting of protected data. It enables data analysis while maintaining security. Users can work with encrypted values without disrupting business processes.
The method offers strong security guarantees. It uses proven cryptographic algorithms. FPE resists various types of cryptographic attacks.
Interested Read: Protect PII and Sensitive Data with Data Tokenization
Exploring Tokenization

Tokenization replaces sensitive data with random tokens. Each token serves as a reference to the original value. The process creates no mathematical connection between tokens and source data.
Modern tokenization supports various data types, handles structured and unstructured information, and scales across different business needs.
Types of Tokenization Methods
PII tokenization provides specific protection for personal data. These implementations secure sensitive identity information, and access controls protect the token-to-value relationships.
The vault system maintains token mappings. It handles token generation and lookup requests. Security measures protect the vault infrastructure.
Vaultless tokenization uses algorithms to generate tokens. It creates consistent tokens without storing mapping tables, reducing storage needs and improving performance.
Advanced Tokenization Features
Dynamic token generation supports real-time processing. The system creates tokens on demand. This feature enables fast transaction processing.
Token formatting rules preserve data usability. Applications process tokens like original data. The system maintains business logic and validation rules.
Benefits of Tokenization
Data tokenization vs encryption shows distinct advantages. Tokenization eliminates sensitive data from systems. Organizations store fewer sensitive values in their databases.
Tokens resist reverse engineering attempts, providing strong protection against data breaches. Stolen tokens hold no value to attackers.
The method supports data analytics needs. Organizations analyze token data safely. Business intelligence processes continue without risk.
Key Similarities Between FPE and Tokenization
Both methods preserve data format and length. They enable business applications to function normally, and users can work with protected values without system changes.
Both solutions support compliance requirements. They protect sensitive information effectively. Integration with existing workflows remains smooth.
Security teams can manage both methods centrally. They support enterprise-wide deployment. Organizations maintain consistent security policies.
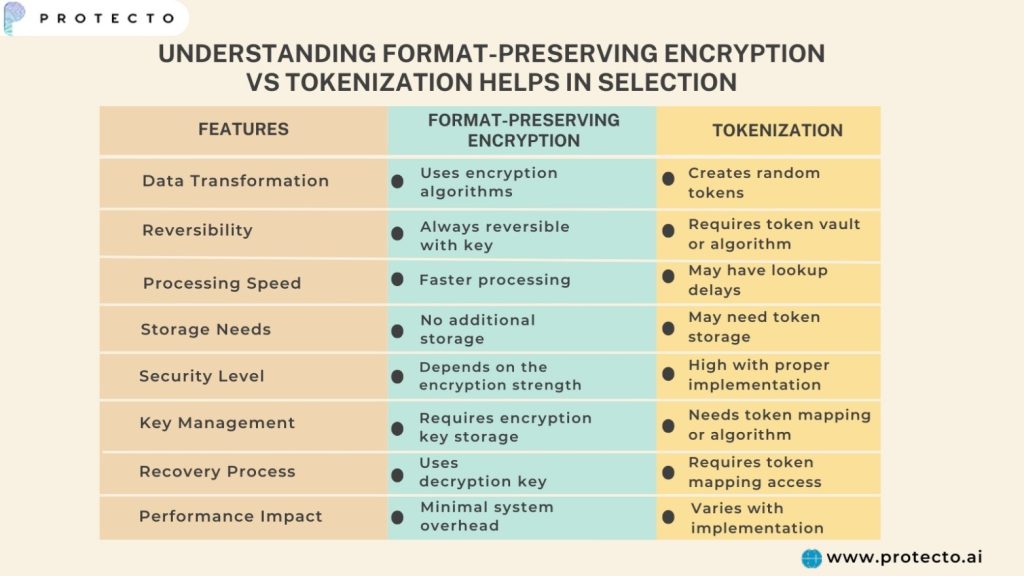
Critical Differences Between FPE and Tokenization
Understanding format-preserving encryption vs tokenization helps in selection:
Interested Read: Pseudonymization vs Anonymization: Key Differences, Benefits, & Examples
Data Security and Compliance
FPE meets PCI DSS requirements for card data. It supports GDPR compliance through solid encryption, enabling organizations to achieve regulatory compliance while maintaining data utility.
Tokenization excels at PCI DSS compliance. It removes sensitive data from scope, and many compliance frameworks accept tokenization as a valid protection method.
Industry Standards Support
Both methods align with security standards. They meet the requirements for data protection with auditors across multiple industries recognizing their effectiveness.
Financial institutions trust these methods. Healthcare organizations rely on their security. Retail businesses protect customer data effectively.
Risk Management Benefits
Protected data reduces breach impacts. Organizations limit exposure to threats. Security teams manage risks more effectively.
Choosing Between FPE and Tokenization

Consider system performance requirements. Format-preserving encryption vs tokenization decisions depend on processing needs. Tokenization suits systems with lower performance demands.
Evaluate existing infrastructure capabilities. FPE requires encryption key management. Tokenization needs token storage or generation systems.
Implementation Factors
Budget constraints affect technology choice. FPE offers lower infrastructure costs. Tokenization may require additional storage investment.
Team expertise influences decisions. Some teams know encryption better. Others have experience with tokenization systems.
Business Requirements
Think about compliance needs. Some regulations prefer specific protection methods. Check compliance requirements before making a choice.
Data access patterns matter. FPE supports faster data retrieval. Tokenization may add lookup steps to processes.
Conclusion
FPE and tokenization offer distinct advantages for data protection. Each method suits different business needs and technical requirements, so organizations must weigh various factors when choosing a solution.
Security teams should evaluate specific needs carefully. Performance, compliance, and infrastructure determine the best choice. Professional guidance helps select the most suitable data protection approach.
Regular security reviews ensure continued effectiveness. Protection methods evolve with threats. Organizations should adapt security measures accordingly, and relying on comprehensive solutions like Protecto can go a long way.