Robust Data Privacy for Healthcare and Life Sciences Companies

HIPAA-Compliant Security
Our advanced data masking algorithms ensure that sensitive Protected Health Information (PHI) remains confidential and secure, adhering to the stringent requirements set by HIPAA.


Impeccable Data Anonymization
Our advanced anonymization approach protects patient identities and ensures healthcare data privacy while preserving the utility of data for performing analysis.”
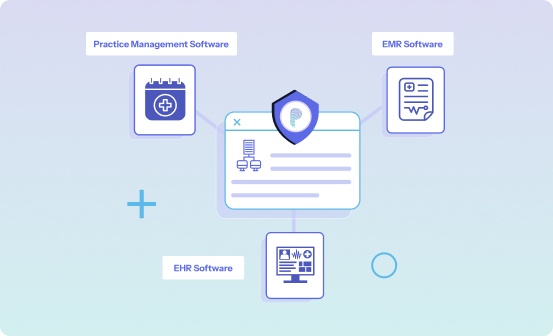
Seamless EHR Integration
Our platform seamlessly integrates with your data sources including EHR, EMR, Practice Management Software, and more making data masking a seamless and efficient process.

Flexible Masking
Protecto empowers you to tailor masking rules according to your specific requirements, ensuring maximum healthcare data privacy, flexibility and control over the process.
Audit Trail for Compliance
Stay audit-ready with our comprehensive audit trails. Easily track and monitor data access and masking activities, providing transparent compliance reporting.

How Protecto works
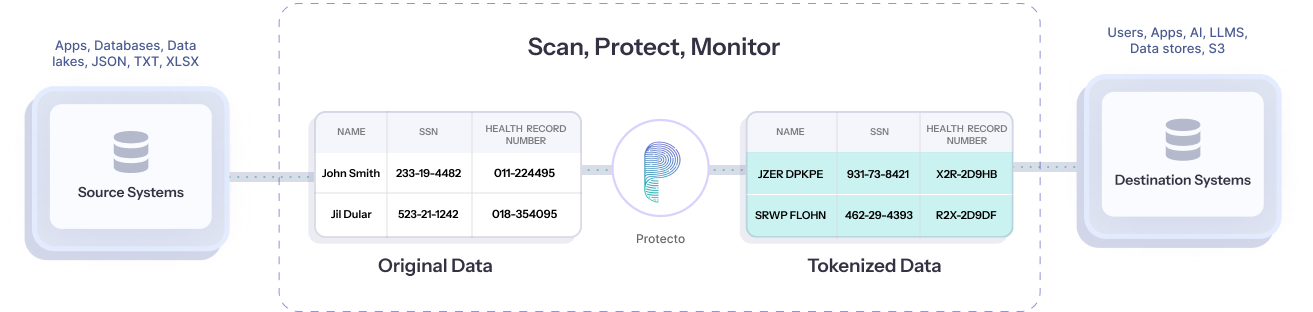
Take the first step towards fortifying healthcare data privacy. Try Protecto for free.
Chief Information Officer
Global Financial Asset Management Company
Easy-to-implement solutions for common healthcare use cases
Our solution for optimum healthcare data privacy is quick to deploy, highly adaptable, and equipped to support your various use cases without compromising sensitive patient data.
Compliance
Achieve compliance standards suitable for auditing, such as HIPAA. Adhere to the established standards for safeguarding personal healthcare data.

Treatment & Care
Accelerate advancements in treatment and care, such as compliant data access through data de-identification, and scalable data accessibility for advanced analytics.

Data Sharing
Ensure the safe exchange of sensitive data with external parties such as clinicians, patient service providers, and other third-party entities.