AI agents process more personal data than traditional apps because their inputs are unpredictable. Businesses handling data of EU residents that adopt these systems must know how GDPR applies to AI agents.
This guide is designed to give you that clarity – what GDPR expects, how AI agents complicate the picture, and what steps you can take so your team can operate with confidence before the next audit, customer security review, or enterprise deal.
Why GDPR Matters Even More for AI Agents
Startups rolling out AI features assume GDPR is a blocker. This is a wrong assumption as GDPR actually helps you design AI systems with clarity, accountability, and trust. Once you understand how the rules map to AI behaviors, the path forward becomes much easier.
It is critical to recognize that compliance begins with visibility. You can’t comply with what you can’t see. Once you map what your AI agents access, store, and generate, everything else becomes manageable.
1. Understanding GDPR Responsibilities for AI Agents
Let’s break down the core GDPR obligations and how they apply to AI agents as clarity makes regulation less abstract and more operational.
Data Minimization: The Agent Should Only Use What It Needs
An AI agent often receives more data than necessary because prompts are often broad. The GDPR requires you to restrict data collection to what is necessary.
We’ve learned that:
- Restricting data at the prompt boundary is one of the easiest early wins. You can do this using control based access control techniques.
- Masking identifiers before the agent sees them reduces both risk and audit complexity.
- Minimization sets you up for simpler subject-access and deletion workflows later.
Purpose Limitation: The Agent Must Know Why It Is Processing Data
If a user shares personal data during a conversation, the agent must use it only for the purpose disclosed to the user.
For example:
- If an agent collects an address for shipping an item, it cannot reuse that address to train a recommendation model.
- If the agent reads an HR document to draft a summary, it should not store those details for future unrelated tasks.
The practical step here is purpose tagging; annotating each workflow with its intended purpose to ensure the agent uses the data exclusively within those boundaries.
Storage Limitation: AI Outputs Can’t Live Forever
AI agents often generate summaries, notes, transcripts, or recommendations containing personal data. GDPR expects you to store them only as long as necessary.
The startups that handle this well:
- Set automatic retention windows for agent-generated content
- Delete intermediate data within minutes
- Allow users to delete their history at any time
This enables your team to prove compliance effortlessly to auditors.
User Rights: Access, Correction, Deletion, Objection
GDPR grants users rights over their data. AI agents complicate this because data might appear in conversation history, embeddings, vector stores, fine-tuning datasets, and logs.
Next, map personal data throughout your AI pipeline to design deletion routines that reach every downstream system.
Accountability: Proof Beats Promises
Regulators and enterprise buyers increasingly expect audit evidence. Evidence includes:
- What the agent accessed
- Why it accessed it
- What transformations occurred
- Where outputs were stored
- Who viewed them
2. How AI Agents Complicate GDPR Compliance
AI agents change how teams think about compliance because they introduce new behaviors that traditional systems never had.
Let’s examine the most common challenges startups encounter.
Challenge 1: Agents Handle Conversations That Contain Unpredictable Personal Data
Humans write naturally without censoring themselves for compliance structures. Conversations usually go like:
- “Here’s my phone number, call me later…”
- “My employee ID is 28492.”
- “The customer’s daughter Emily attends Ridgewood Elementary.”
This conversational variability breaks regex-based PII detection. GDPR compliance requires understanding meaning and not just patterns.
Contextual detection models help here. And we’ve learned that deploying them early prevents hundreds of small exposures you’ll never hear about because they never happened.
Challenge 2: Data Leaks Into Logs, Prompts, and System Messages
Many teams use verbose prompts while prototyping. Some include example customer data. Others store conversation logs indefinitely for debugging.
These logs become part of your data landscape, and therefore part of your GDPR responsibilities.
A calm, pragmatic fix:
- Mask sensitive fields before logging
- Set retention windows for debug logs
- Separate development logs from production
Once implemented, these changes rarely affect productivity—yet they reduce audit-time complexity by an order of magnitude.
Challenge 3: Agents Often Work Across Systems, Creating Hidden Data Flows
One AI agent might:
- Pull CRM data
- Query a knowledge base
- Hit an email API
- Generate a summary stored in a ticketing system
Each hop creates a trace of personal data. If a user enters a prompt asking for a certain dataset, the AI may inadvertently pull up data from files they are not authorized to view.
Challenge 4: Training and Fine-Tuning Pipelines Might Capture Personal Data
Even if you don’t plan to store training data, a single misconfigured sync can populate datasets with PII. In this case, the challenge isn’t fixing or removing PII from the pipeline; it’s proving you fixed it.
A strong data governance layer ensures:
- No personal data enters training pipelines without approval
- Sensitive fields are consistently masked or tokenized
- Review logs show exactly what was ingested and when
Challenge 5: Subject-Access Requests Become Harder When AI Is Involved
If a user requests, “Delete all information you have about me,” traditional databases are straightforward to scan.
AI systems are different:
- Embeddings contain semantic traces
- Vector databases mix thousands of users’ content
- Generated outputs might reference details from multiple sources
Yet GDPR still requires you to produce or delete the data. This is where structured metadata and data lineage become essential. By tagging user data at ingestion, you make retrieval trivial later.
3. A Practical Framework for GDPR-Compliant AI Agents
To help startups operationalize GDPR without slowing down innovation, here’s a framework we use during deployments. Each step is designed to deliver clarity and forward momentum.
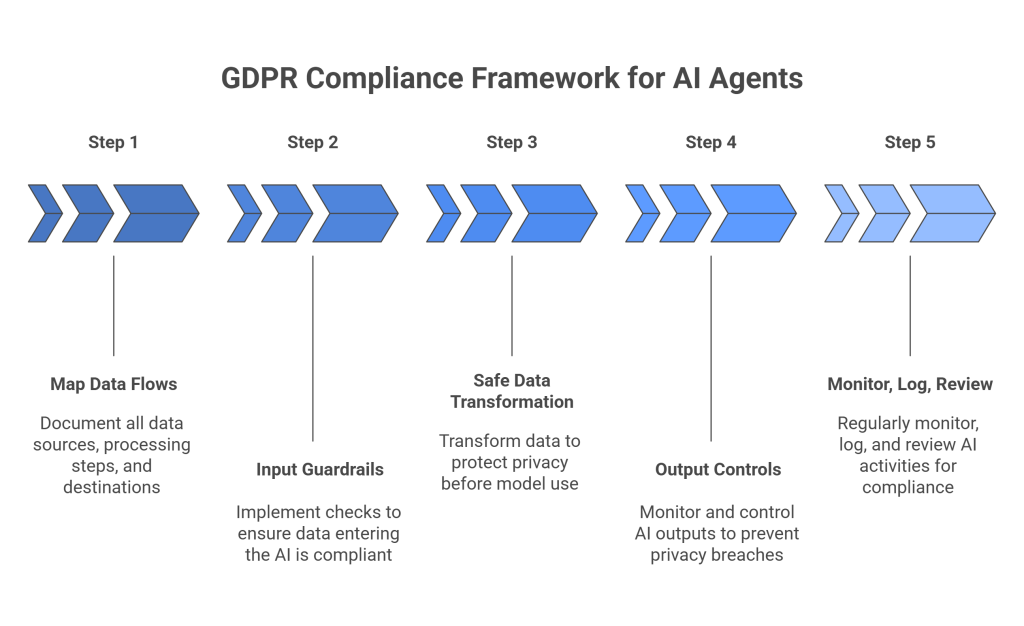
Step 1: Map data flows end-to-end
Start with a simple diagram answering three questions:
- What data enters the AI agent?
- Where does it go next?
- Where does it persist?
Track every script, domain, and data flow. With Protecto you’ve got the tools to make that happen, but the principle stands even without tooling: visibility comes first.
Most teams discover 2–3 unexpected pathways. Fixing those early prevents dozens of downstream issues.
Step 2: Implement input guardrails
Before data reaches the model, apply:
- PII detection
- Role-based filtering
- Contextual masking
- Purpose tagging
These guardrails reduce risk instantly because they limit what the agent can see. The outcome: cleaner prompts, safer data exposure, and simpler audits.
Step 3: Transform data safely before it reaches the model
When personal data is required by the use case, ensure it’s transformed with:
- Masking for identifiers
- Tokenization for reversible fields
- Encryption for persistence
We’ve learned a thing or two deploying this over 100 times. Teams consistently find that preprocessing is the easiest moment to eliminate 80% of long-term compliance complexity.
Step 4: Build output controls
Even if the model behaves correctly, GDPR expects you to manage what happens after generation.
Add measures like:
- Automatic redaction of sensitive details
- Time-limited storage of generated summaries
- User-facing deletion controls
This provides users with visible control, an essential part of GDPR trust.
Step 5: Monitor, log, and review regularly
Compliance is not a one-time task. Set up:
- Logs showing who accessed what
- Alerts for unusual data flows
- Reviews after each model update
- Automated reports for audits
Always-on monitoring, when done right, works quietly in the background. It reduces surprises and enables your team to respond quickly when needed.
4. Four Misconceptions Startups Have About GDPR and AI
Let’s examine misconceptions we hear frequently—and what the regulation actually expects.
“If we don’t store outputs, we’re exempt.”
AI agents may still process personal data even if they don’t store it. GDPR applies to processing, not just storage.
“Embeddings don’t count as personal data.”
They often do. If embeddings can be linked back to an identifiable person, they fall under GDPR.
“We use a third-party LLM, so responsibility is theirs.”
Third-party vendors act as processors, but you remain the controller. This means GDPR responsibilities stay with you—including user rights.
“GDPR will slow down our AI roadmap.”
In practice, the opposite happens. Once workflows are structured and predictable, teams build faster because they spend less time fixing issues retroactively.
5. A Practical Compliance Checklist for AI Agents
Here’s a lightweight guide your team can use this week.
Data Flow Mapping
- All inputs, outputs, logs, and storage locations mapped
- Third-party processors documented
Pre-Processing Controls
- PII detection at ingestion
- Data minimization enforced
- Sensitive fields masked or tokenized
Model Interaction Controls
- Purpose tagging applied
- Prompts scrubbed of unnecessary data
Post-Processing Controls
- Output retention policies defined
- Users can delete history
- Data stored only where needed
User Rights
- SAR retrieval automated
- Correction and deletion workflows tested
- Objection requests supported
Accountability & Logging
- Logs capture who accessed what and why
- Regular reviews scheduled
- Incident response playbooks prepared
How Protecto Solves GDPR Challenges for Startups Using AI Agents
What we’ve learned working with dozens of early-stage teams is that AI agents don’t create new GDPR or privacy rules – they just make existing ones harder to manage.
Protecto solves these challenges by adding structure, visibility, and automatic enforcement around how AI agents handle personal data. Here’s how it helps at each stage of the AI agent lifecycle.
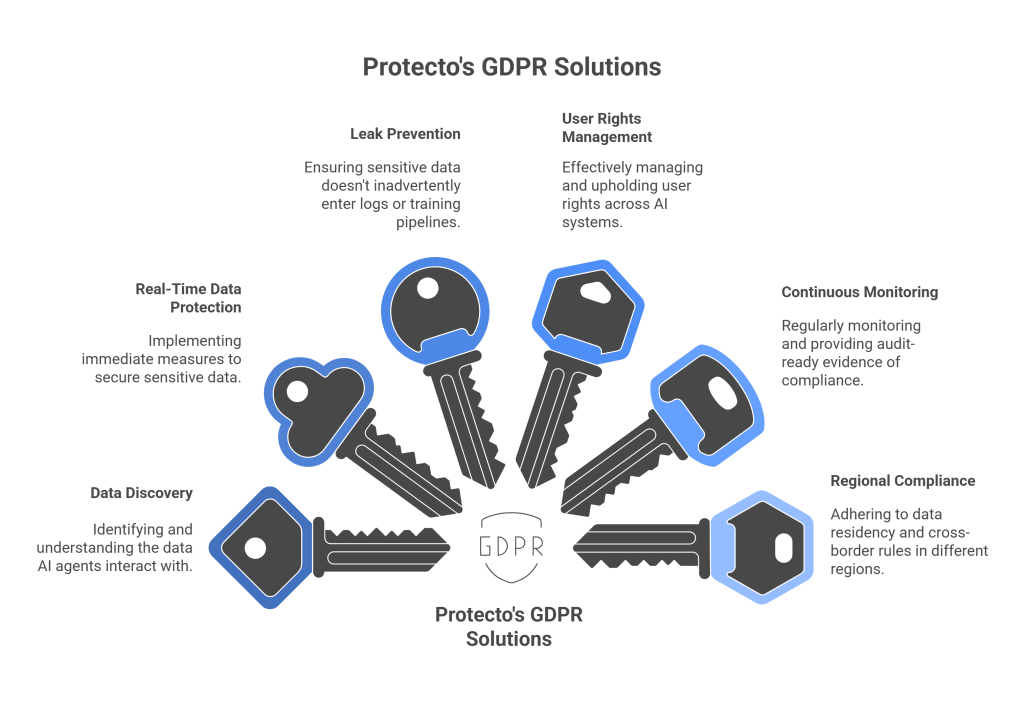
1. Discovering What Data AI Agents Actually Touch
Most teams underestimate how much personal data flows through their agents. Protecto:
- Maps every data source your agents access
- Detects PII/PHI in unstructured text, transcripts, emails, chats, and docs
- Finds hidden data flows you didn’t know existed
- Shows exactly where personal data enters your AI pipeline
This visibility alone eliminates 30–50% of compliance uncertainty.
2. Real-Time PII Redaction, Masking, and Tokenization
Protecto transforms sensitive data before it ever reaches an AI system. It automatically:
- Redacts PHI and sensitive context from unstructured inputs
- Masks names, emails, phone numbers, and IDs
- Tokenizes identifiers so the model can function without seeing raw data
This reduces risk without affecting performance because it receives structured, consistent, privacy-safe input.
3. Preventing Sensitive Data From Leaking Into Logs, Prompts, and Training Pipelines
AI agents leave traces in logs, summaries, vector embeddings, support replies, emails. Protecto prevents leakage through:
- Output scanning for PII before content is stored or shared
- Automatic redaction of sensitive details in generated replies
- Retention policies that delete stored outputs after a defined period
- Debug logs scrubbed before persistence
4. Managing User Rights Across AI Systems
Subject-access requests (SARs) become tricky when data moves through embeddings, vector stores, transcripts, summaries, chat logs, and fine-tuning sets.
Protecto handles this by:
- Tracking user-linked data from ingestion to output
- Letting you retrieve all data for a user in seconds
- Allowing deletion across every agent touchpoint
- Maintaining lineage so you can prove what was deleted
5. Continuous Monitoring and Audit-Ready Evidence
Startups often struggle most with GDPR’s accountability requirement—proving what happened.
Protecto provides:
- Logs showing who accessed what personal data and why
- Real-time alerts when agents encounter unexpected PII
- Reports aligned to GDPR, SOC 2, HIPAA, and enterprise reviews
- Privacy posture dashboards for board decks and investor diligence
This is the “quiet background protection” that helps teams stay compliant without slowing down.
6. Regional Compliance (Data Residency, Cross-Border Rules)
AI agents often pull data from systems in different regions, which complicates GDPR and international transfers.
Protecto helps by:
- Enforcing region-specific data routing
- Ensuring AI agents only process EU data within the EU
- Applying local PII rules (GDPR, CCPA, LGPD, etc.) depending on region
- Generating region-aware audit evidence