Overview of LLM Security Challenges
Large Language Models (LLMs) transform how organizations process and analyze vast amounts of data. However, with their increasing capabilities comes heightened concern about LLM security.
The OWASP Top 10 for LLMs offers a guideline to address these risks. Originally designed to identify common vulnerabilities in web applications, OWASP has now extended its focus to AI-driven technologies. This is essential as LLMs are prone to unique LLM vulnerabilities that traditional security measures may overlook.
Attackers can exploit weaknesses, manipulate models through input manipulation, and even extract sensitive information from poorly designed systems. Understanding and mitigating these risks is critical to ensuring robust LLM security in any enterprise that leverages artificial intelligence.
By following frameworks such as OWASP AI Top 10, organizations can protect themselves against common attacks while strengthening their AI deployments for the future.
What is OWASP?
The Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) is a globally recognized nonprofit organization dedicated to improving software security. It provides free tools, frameworks, and resources to help developers identify and mitigate security risks in their applications. OWASP is best known for its OWASP Top 10, a list of the most critical vulnerabilities in web applications.
The OWASP AI Top 10 is a specific adaptation to highlight vulnerabilities common in LLM applications.
What is the OWASP Top 10?
The OWASP Top 10 is a globally recognized guide highlighting the most critical security risks to web applications. It is regularly updated to reflect emerging threats and provides developers with insights on the most pressing vulnerabilities. The primary goal of this list is to help organizations understand the risks associated with insecure applications and implement security measures to address these threats.
Regarding LLM security, the OWASP Top 10 for large language model applications introduces a tailored version of this framework, focusing specifically on vulnerabilities unique to LLM applications.
The OWASP AI Top 10 for LLMs identifies common vulnerabilities and offers practical mitigation techniques to help developers secure their AI systems.
OWASP Top 10 for Large Language Model Applications with Examples
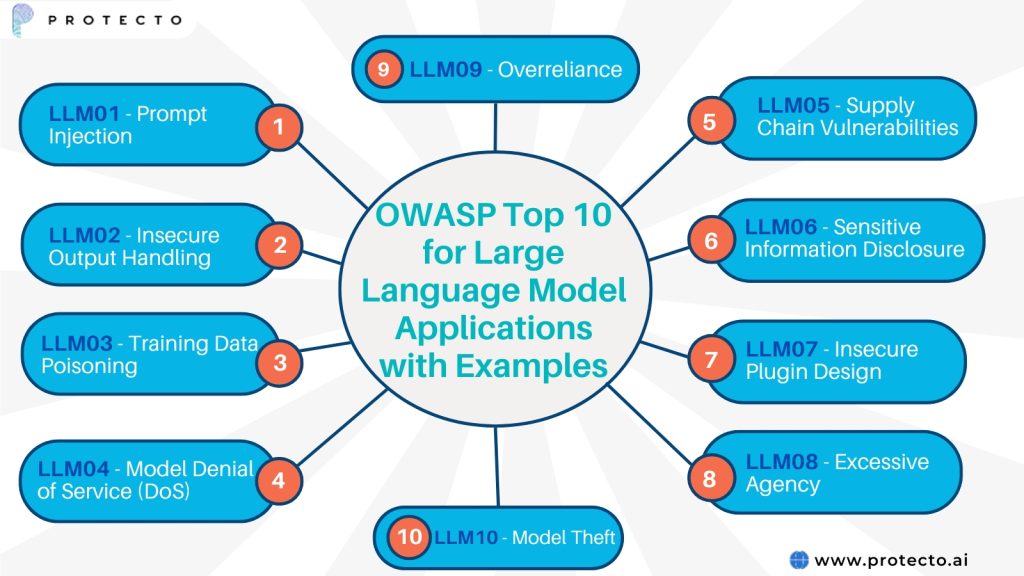
The OWASP Top 10 for large language model applications outlines key risks unique to LLM security and provides mitigation strategies.
LLM01 – Prompt Injection
Prompt injection is one of the most prevalent risks in LLM security. Attackers exploit the model by manipulating inputs (prompts) to trigger unintended actions or responses.
Consider an LLM used for customer support. If an attacker submits a cleverly designed query, it could lead the model to leak sensitive information or generate fake customer responses. Mitigating prompt injection requires strict input validation and monitoring.
LLM02 – Insecure Output Handling
Insecure output handling occurs when LLMs produce sensitive or harmful content that isn’t adequately managed. This can lead to data breaches or disseminating incorrect or damaging information.
An example would be a chatbot in a hospital setting providing too much information based on vague queries. The solution is to apply filtering mechanisms that sanitize the model’s output, ensuring only safe and appropriate information is shared.
LLM03 – Training Data Poisoning
Training data poisoning happens when attackers manipulate or inject malicious data during the model’s training phase. This can compromise the integrity of the LLM and lead to biased or incorrect predictions.
To prevent training data poisoning, developers should implement strict validation and monitoring of the data sources used for training and regularly audit the datasets for any anomalies.
LLM04 – Model Denial of Service (DoS)
A Model Denial of Service (DoS) attack involves overwhelming the LLM with a high volume of requests, causing it to crash or become unresponsive. This could disrupt services that rely on the model for real-time data processing or customer support.
A prime example of this would be an LLM used in e-commerce suddenly becoming unresponsive during a sale due to a DoS attack. The best way to address this vulnerability is by implementing rate-limiting measures and using security layers that detect and block abnormal traffic patterns.
LLM05 – Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
Supply chain vulnerabilities arise when third-party components, libraries, or external data sources used by LLMs are compromised. These can introduce malware or other security threats into the LLM environment.
Addressing supply chain vulnerabilities involves rigorous vetting of all external components and regularly updating libraries to patch known security issues.
LLM06 – Sensitive Information Disclosure
Sensitive information disclosure is a common risk in LLM security. It occurs when LLMs unintentionally reveal confidential data, either through their outputs or by being manipulated to extract hidden information.
An example would be a model used by a financial institution inadvertently leaking transaction data due to poorly configured output handling. Encryption, regular audits, and strict access controls are essential to mitigate this risk.
LLM07 – Insecure Plugin Design
Insecure plugin design refers to vulnerabilities introduced by third-party plugins or extensions that enhance LLM functionality. Plugins not correctly secured can create backdoors, enabling attackers to compromise the model.
For instance, a plugin that integrates LLMs into a content management system (CMS) could allow attackers to manipulate content or inject malicious code. Ensuring that all plugins are adequately vetted, sandboxed, and monitored is crucial for preventing this attack.
LLM08 – Excessive Agency
Excessive agency refers to giving LLMs too much control over decision-making processes, especially in critical applications. If a model is given excessive autonomy without human oversight, it could lead to unintended actions with severe consequences.
An example would be an LLM for automating financial transactions, where the model makes high-risk decisions without proper checks. Limiting the model’s decision-making abilities and incorporating human oversight into crucial processes are essential to mitigate this risk.
LLM09 – Overreliance
Overreliance on LLMs can create significant risks, especially if organizations fail to account for the limitations of these models. Relying too much on LLMs without understanding their potential weaknesses can lead to errors, misjudgments, or security lapses.
For example, an organization might overly depend on an LLM for legal document drafting, but the model could introduce inaccuracies or omit critical information. Implementing fallback mechanisms and using LLMs as assistive tools rather than primary decision-makers can help mitigate this vulnerability.
LLM10 – Model Theft
Model theft occurs when attackers extract or copy a proprietary LLM for their own use, potentially reversing engineering it to exploit vulnerabilities or use it for malicious purposes. This is a serious risk, particularly for organizations that invest heavily in custom LLM development.
A real-world scenario could involve a competitor stealing a company’s proprietary language model and using it for commercial gain. Encryption, model watermarking, and strong access controls are vital measures to prevent model theft.
OWASP LLM Checklist for LLM Vulnerabilities Suggested by OWASP
Mitigating LLM vulnerabilities requires a systematic approach. OWASP offers a comprehensive checklist to help secure LLM applications and safeguard against potential risks.
Regularly Monitor and Audit Access Logs and Activities
Consistent monitoring of access logs is crucial in detecting unusual behavior. Auditing access helps identify potential security breaches before they escalate. Monitoring activities also ensure that LLM security remains intact, especially in large data processing environments.
Implement Strong Access Controls and Authentication Mechanisms
Access to LLMs should be restricted to authorized personnel only. Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) and role-based access controls helps prevent unauthorized users from exploiting the system. Robust authentication mechanisms ensure that sensitive data stays protected.
Enhance the Model with Fine-Tuning or Embeddings
LLM models can be improved through fine-tuning or using embeddings to address specific vulnerabilities. This process helps tailor the model’s capabilities and strengthens its defenses against known threats, reducing the chances of exploitation.
Integrate Adequate Data Sanitization and Scrubbing Techniques
To prevent injection attacks, it’s important to sanitize all input data. Implementing data scrubbing techniques ensures that malicious content within input prompts or external data is identified and neutralized before interacting with the LLM.
Implement Input Validation
Validating input data is critical to maintaining LLM security. By ensuring that all data inputs follow strict validation rules, organizations can significantly reduce the risks associated with prompt injection and other forms of input manipulation.
Based on the OWASP top 10 for LLM applications, this checklist provides actionable steps that organizations can take to protect their LLM systems.
Best Practices for Keeping LLMs Secure
Organizations must adopt a range of LLM security best practices that address vulnerabilities identified in the OWASP Top 10 for LLM applications. Regular updates and patches are essential to prevent supply chain vulnerabilities and ensure the LLM stays current against evolving threats.
Implementing strict access controls, such as role-based permissions and multi-factor authentication, helps limit unauthorized access to sensitive data and model operations. Input validation and data sanitization processes should be rigorously applied to avoid prompt injection attacks and other input manipulation. Additionally, constant monitoring and auditing of LLM activities can identify suspicious behavior early, reducing risks like model theft or denial of service.
By combining these best practices with OWASP’s guidelines, organizations can strengthen LLM security and ensure resilience against potential attacks.
Conclusion
Securing LLM applications is essential in today’s AI-driven world. By incorporating OWASP’s Top 10 for LLMs, businesses can proactively address critical vulnerabilities. These practices are crucial for safeguarding sensitive data and maintaining robust LLM security.



